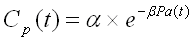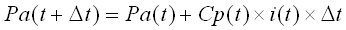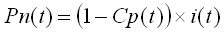Horner Model
The Horner runoff volume model is used to determine net rainfall on urban subcatchments. The model was developed for use on impervious surfaces in medium sized subcatchments.
The Horner model takes into account the decrease in rainfall losses on impervious surfaces throughout the rainfall event via a loss coefficient, cp. Loss coefficient, cp, is related to the ruggedness of roads, potholes etc. cp decreases with time and is not constant.
|
|
where: Cp is the loss coefficient Pa is the cumulative loss (mm) t is the time from the beginning of the run (hours) It is assumed that for t=0, Pa=0, therefore Cp(t=0) = a |
The cumulative loss, Pa is defined as:
|
|
where: i is the rainfall intensity |
The net rainfall intensity, Pn, in mm/hr is then:
|
|
|
During dry conditions, the infiltration capacity of the subcatchment recovers after a period T of dry weather. The cumulative loss, Pa, decreases linearly with time, and the loss coefficient, cp, increases exponentially.
During dry conditions:
|
|
where: Pa(twet) is Pa at the end of the wet conditions twet is the time at the end of the wet conditions tcurrent is the current time Trecovery is time to recover to initial conditions |