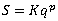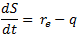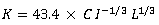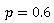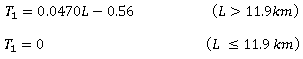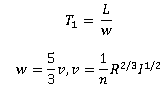Non-Linear Routing Model
The Non-linear routing model routes flow using the Storage Function Method, used as a standard runoff model in Japan.
See the Japanese Runoff Methodology technical paper for further information.
The basic equations of the method are as follows:
|
|
where: S: facade storage water depth in a river basin (mm) K, p: characteristic coefficients of basin q: runoff depth (mm/hr) re: intensity of effective rainfall (mm/hr) |
To use the Non-linear routing model in InfoWorks ICM, set the Routing model field for the Runoff Surface to Non-linear.
The parameters for setting coefficients K and p are defined in the subcatchment properties (see Routing method below). Lag time is also defined in the subcatchment properties (see Lag time method below).
Routing method
Parameters for setting coefficients K and p are defined in the Subcatchment Data Fields.
To set K and p values, select a Non-linear routing method for the subcatchment:
- User - enter user defined values for Storage factor K and Exponent p data fields
- Izzard - calculate K and p using the Izzard method (see below)
- Equivalent roughness - calculate K and p using the Equivalent roughness method (see below)
Izzard method
The basic equations of the Izzard method are:
|
|
where: C: equivalent roughness coefficient of basin I: catchment slope (m/m) L: catchment length (km) |
The values in the following subcatchment data fields are applied when using the Izzard method:
- Equivalent roughness (C)
- Slope (I)
- Dimension (L)
Equivalent roughness method
The basic equations of the Equivalent roughness method are:
|
|
where: N: equivalent roughness I: catchment slope (m/m) L: catchment length (km) |
The values in the following subcatchment data fields are applied when using the Equivalent roughness method:
- Equivalent Manning's n (N)
- Slope (I)
- Dimension (L)
Lag time method
Parameters for setting lag time are defined in the Subcatchment Data Fields.
To set the lag time value, select a Lag time method for the subcatchment:
- User - enter user defined values for Lag time, tl data field
- Kimura - calculate lag time using Kimura method (see below)
- Flood velocity - calculate lag time using Flood velocity method (see below)
Kimura method
The basic equations of the Kimura method are:
|
|
where: T1: lag time (hr) L: catchment length (km) |
The values in the following subcatchment data fields are applied when using the Izzard routing method:
- Dimension (L)
The lag time calculated is converted from hours into minutes.
Flood velocity method
The basic equations of the Flood velocity method are:
|
|
where: T1: lag time (s) L: catchment length (m) I: catchment slope (m/m) n: equivalent roughness R: hydraulic radius (m) |
The values in the following subcatchment data fields are applied when using the Flood velocity method:
- Equivalent Manning's n (n)
- Slope (I)
- Dimension (L)
The lag time calculated is converted from seconds into minutes.