Pumps (InfoWorks)
A pump is controlled by the switch-on and switch-off levels for the water level in the upstream node (the wet well). The units for these levels are level above system datum.
The pump will start operating when the water level in the node rises above the switch-on level, and will continue running until the water level falls below the switch-off level. The switch-on level must be greater than the switch-off level.
A pump always pumps from upstream to downstream. Therefore, it is important to choose the direction of flow of the control link correctly.
Types of pump characteristics
The following types of pump characteristics can be defined in InfoWorks ICM:
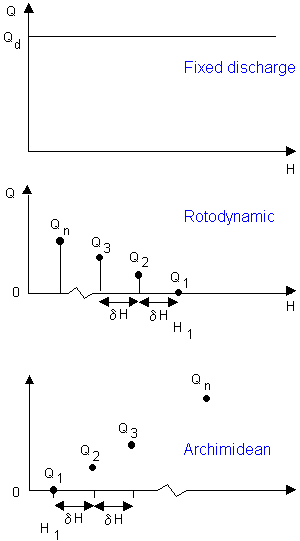
- Fixed discharge pump. The fixed discharge is independent of the head on the pump. This is suitable for small dry weather flow pumps.
- Rotodynamic pump. A characteristic curve is defined as a table of discharges for a range of heads across the pump. InfoWorks ICM defines the head as the difference between the water level in the upstream node and the pressure head in the downstream rising main.
- Variable frequency drive pump. A variable speed rotodynamic pump. The head-discharge curve defined applies to the nominal speed of the pump. The actual speed of the pump is defined by the use of RTC.
- Variable speed pump. This is a continuous regulator, whose regulated parameter is its discharge.
- Archimedean screw pump. This pump is independent of the downstream head but has a discharge that increases with the upstream water level. The pump is defined as a table of values of discharge for a range of upstream water levels.