Locating Smoke Defects from Distance Measurements
There are two methods that can be used to determine the location of Smoke Defect Observations:
- Fixed Point Method
- 90 Degree Method
Fixed Point Method
The fixed point method uses distances from two known points (e.g. buildings) to identify the location.
The Survey Triangulation Tool can be used to determine the location of smoke defects surveyed by the fixed point method.
90 Degree Method
The 90 degree method uses the distance from a manhole (upstream or downstream) along the pipe, in conjunction with the perpendicular distance from the pipe to the defect.
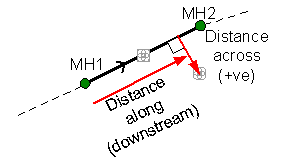
InfoAsset Manager can calculate the X and Y coordinates of a smoke defect, given the following information:
- Direction (Upstream / Downstream)
- Distance along pipe (longitudinal distance from upstream / downstream node)
- Distance across pipe (lateral distance, where positive value is right perpendicular from the pipe, negative value is left perpendicular from the pipe facing the Direction specified)
These measurements can be entered in data fields on Smoke Defect Observation Grid Window of the Survey Grid or on the Position Page of the Smoke Defect Observation Property Sheet.
For InfoAsset Manager to calculate the X and Y coordinates of a smoke defect:
- The smoke defect must be associated with a Smoke Test Survey
- The Smoke Test Survey must have a surveyed pipe reference
- The X and Y coordinate fields of the smoke defect must be flagged #D
X and Y coordinates are calculated based on the straight line between the start and end of the associated pipe.
