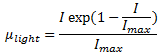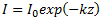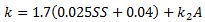Solar Radiation
When modelling Algae, it is necessary to specify the amount of solar radiation at the water surface. This affects the light induced growth limitation factor for the algae, and also for macrophytes, if these are simulated as well. The light limitation factor is a function of the solar radiation, total concentration of sediment fractions and algal concentrations.
A single solar radiation profile can be defined in a Rainfall Event. Linear interpolation is carried out between profile values.
Solar radiation acts in processes for the following objects:
- River reaches
- Channels
- Open conduits
- Storage nodes and ponds (where last level entry is at or above ground level)
- 2D elements
Solar radiation is not active for the following objects:
- Closed conduits
- Bridge openings
- Storage nodes (where last level entry is below ground level)
- Manholes
- Break nodes
Equations
The light induced growth limitation factor for algae is calculated from the following equation:
|
|
where: mlight = light limitation factor at hydraulic mean depth, z, below the surface I= intensity of light at hydraulic mean depth, z, below the surface Imax = light intensity which will produce maximum productivity
Imax is defined in the Water Quality and Sediment Parameters as Solar radiation (maximum productivity). |
The light intensity at depth, z, is given by the Beer-Lambert law:
|
|
where: I0 = light intensity at the surface k = light attenuation factor which is a function of the total sediment fraction and algae concentrations:
SS = total concentration of sediment fractions (mg/l) A = algal concentration (mg/l) k2 = extinction coefficient relating to algal concentrations |
Because of the effect of salinity on the flocculation of mud particles the light attenuation factor is calculated by the following equation when the salinity exceeds 2ppt:
|
|
|
The equation for light limitation is integrated over the depth to give an average value for the whole water column.