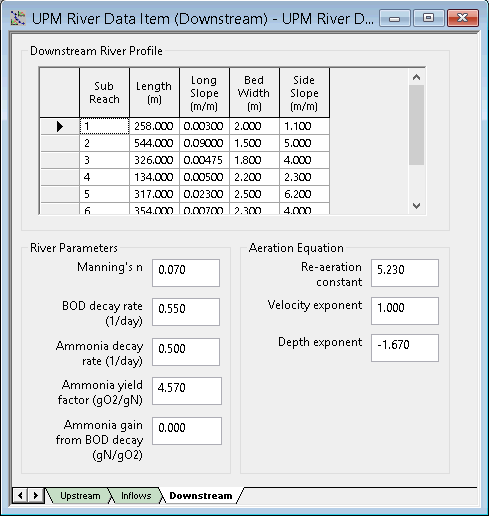
UPM River Data - Downstream View
The Downstream tab on the UPM River Data dialog allows you to enter information relating to the river immediately downstream from the CSOs (combined sewer outfalls).

The information on this tab is required only if you are performing dissolved oxygen impact assessments.
The UPM River Data dialog is displayed when you open an existing UPM river data item by either double-clicking on the item in the model database tree or by right-clicking on it and selecting Open from the context menu.
Downstream River Profile
The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water is affected by the river profile. You should enter parameters for up to forty sub-reaches, representing the river profile downstream from the CSOs. Note that the cross-sectional profile of each sub-reach is assumed to be trapezoidal and symmetrical. Select sub-reaches to represent significant changes in the slope of the river bed or its width.
The following fields must be specified for each sub-reach:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
| Sub-Reach |
The sub-reaches are automatically numbered from the start of the reach, with sub-reach 1 being immediately downstream from the CSOs. |
| Length | The length of the sub-reach. |
| Long Slope | The average water surface slope over the length of the sub-reach. |
| Bed Width | The average width of the river bed in the sub-reach. |
| Side Slope |
The average side slope for the reach. It is assumed that the slope is the same for both sides of the river. For a vertical side, enter 100. |
River Parameters
For dissolved oxygen impact assessments, you must enter the following parameters relating to the river downstream from the CSOs:
|
Field |
Description |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manning's n | The Manning's n value for the reach. | |||
| BOD Decay Rate |
The decay rate per day for BOD. All BOD is assumed to remain in the water column. The change in BOD over time is calculated from:
|
|||
| Ammonia Decay Rate | The decay rate for ammonia. | |||
| Ammonia Yield Factor | The amount of oxygen consumed by nitrification (normally given as 4.57 gO2/gN). | |||
| Ammonia Gain from BOD Decay | The net gain in ammonia due to BOD decay. This is the difference between the ammonia released during BOD decay and the uptake of nitrogen by bacteria involved in BOD decay. |
Aeration Equation
Re-aeration of the water is calculated using the following equation:
|
|
where: K2 is the re-aeration factor, corrected for temperature Cs is the saturation concentration of DO at a given temperature DO is the initial dissolved oxygen in the river |
The re-aeration factor is calculated from:
|
|
where: v is the flow velocity d is the water depth a, b and c are constant The three constants used in the calculation of K2 must be entered as follows:
|