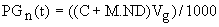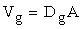Gully Pot Pollutant Build-Up
This topic describes the method for calculating initial pollutant concentrations in gully pots before and during a simulation. The calculation is carried out for each subcatchment. Only dissolved pollutants are modelled in gully pots. Sediment build-up is not taken into account.
The basic hypothesis underlying pollutant build-up is the time-linear accumulation of each pollutant in a gully pot.
InfoWorks ICM uses the same equation to calculate buildup during the Buildup Time and for each timestep during the simulation.
The water quality calculations may not take place on every hydraulic timestep. The calculation frequency depends on the value set for the QM multiplier field on the QM Parameters Dialog.
The actual concentration of each pollutant is calculated by using this formula to find the projected mass of each pollutant without flushing, and then subtracting the mass flushed out into the network. See Surface Washoff and Gully Pot Flushing for more.
The following equation is used:
|
|
where: PGn(t) (kg) is the initial dissolved pollutant mass in the gully pot or the projected pollutant mass at the end of the timestep. C is the initial pollutant concentration in mg/l. Enter the value of C for each Gully Pot Equation on the Surface Pollutant Editor.
M is the gradient of linear accumulation in mg/l day. Enter the value of M for each Gully Pot Equation on the Surface Pollutant Editor. ND (days) is the dry weather buildup period or the timestep length. Vg is the gully pot volume in m3. See below. |
The magnitudes of C and M will vary depending on the Pollution Index. In addition, the values differ for each pollutant type.
An overall gully pot volume is defined for each subcatchment:
|
|
where: Vg is the gully pot volume in m3. Dg is overall gully pot depth (m). Enter a value for Dg for each Pollution Index defined in the Surface Pollutant Editor. A is the area of Runoff Surface 1 (in m2) defined in the Land Use definition. By convention, Runoff Surface 1 is used for the road surface. |
 Water Quality
Water Quality