What's New in Version 11.0 - May 2020
This topic lists all the additions and improvements incorporated in InfoWorks ICM 11.0 which were not available in previous versions.
River reach - Build all
River reaches in InfoWorks networks now have a 'build all' feature which combines the Build sections from lines, Build banks from selected lines, Create bank lines from section ends, Build boundary from banks and section ends, and Build bank connections options in a single operation. See River Reach Building Tools for further information.
River reach - Build banks from selected lines
Previously, when building bank profiles from selected bank lines, you were restricted to only being able to select a maximum of two bank lines at a time. This restriction has been removed. See River Reach Building Tools for further information.
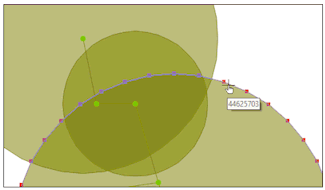
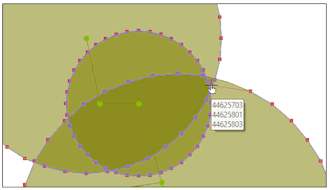
River reach - Left and right bank selection for results
When you use the Graph ( ) or Grid (
) or Grid ( ) pick tool to select a left or right bank on an InfoWorks network, you will now be asked, for the selected bank, the attributes you would like to view the results of. Previously you would have been asked which bank (left or right) you wanted to view the results of (regardless of having already clicked on it on the GeoPlan), before being asked which attributes you wanted to view.
) pick tool to select a left or right bank on an InfoWorks network, you will now be asked, for the selected bank, the attributes you would like to view the results of. Previously you would have been asked which bank (left or right) you wanted to view the results of (regardless of having already clicked on it on the GeoPlan), before being asked which attributes you wanted to view.
Alternative method for mesh generation
A new prototype meshing method, which provides improvements in terms of performance and robustness for complex and closely related geometries, and that utilises available hardware improvements, is now available for generating 2D meshes. A new Mesh generation option has been added to the 2D Zone properties which allows you to choose which method - Classic (the existing method) or Clip meshing (the new prototype method) - you want to use when running an InfoWorks simulation.
Classic meshing is a well-proven method that is fast and robust in the vast majority of cases, but there are exceptions that could present difficulties. Clip meshing should excel by comparison when it encounters highly complex geometry with a vertex density far greater than the desired mesh element density. It does this by first generating a primary mesh, populating the 2D zone with elements that conform to the user's desired element sizes, initially ignoring all other input objects. Then it undertakes a second stage where each primary mesh element is intersected with and "clipped" by any proximal input meshing object. The resultant clipped portions are then recombined into elements suitable for 2D analysis. This can result in a significant reduction in the number of base triangles. In a situation where multiple objects are very approximately coincident, Classic meshing would have had to create triangles small enough to occupy the nearly negligible separation space; this process could be costly, and could potentiality hinder the computational performance of later stages of the meshing algorithm.
Existing 2D zones are automatically assigned the Classic mesh generation method, which can be changed as required. If you want to make Clip meshing the default for new 2D zones, you can do so by changing the user-defined default for the network.
Whilst the new Clip meshing method is intended to provide notable improvements, please be mindful of its prototype status as it is still in a developmental stage; it should not be expected to be fully robust in all cases and as such, careful review of its outputs is recommended. Any feedback on this, or any other feature, is very welcome.
Importing gridded ground models
InfoWorks ICM can now import mixed resolution files, in asc or txt format, with tiles smaller than 1 metre. See Importing and Exporting Gridded Ground Models for further information.
Snapping mode
When the snapping mode is on, and a vertex being moved becomes close to other objects that it can snap to, the vertices in the adjacent objects, including any overlapping ones, will now also be highlighted. This helps, for example, to position a vertex being moved more precisely.
User defined engineering validation
You can now define your own rules for engineering validation for InfoWorks networks using simple syntax similar to SQL statements. Two tabs have been added to the Engineering Validation dialog; a Built In tab that displays the default engineering rules supplied with ICM, and a User Defined tab that can be used to add new or edit existing user defined validation rules defined in the new Validation Rule Editor dialog. See the User Defined Validation Rules for information about setting up user defined rules.
Base time for InfoWorks runs
A base time and date can now be used to define the epoch for all relative times in events. A new Use base time check box has been added to the Run dialog that, when checked, allows you to specify a time and date that is to be used as a base time for a simulation. See the Schedule Hydraulic Run View topic for further information.
Suggest a feature
A new Suggest a feature option has been added to the
HYDX network import
Network data in the HYDX file format can now be imported into an InfoWorks network. Data from the various csv files which comprise a HYDX network are imported to node, link and subcatchment types of objects in InfoWorks ICM. In addition, waste water events can also be imported as database items. See the HYDX Conversion Notes topic for details about the conversion of the imported files.
Hong Kong (5th edition) design rainfall
Design rainfall now includes a new Hong Kong (5th edition) option. See the Design Rainfall Generators and the Rainfall Generator Dialog topics for further information.
Support for ArcGIS 10.8
See Changing the Current Map Control for further information on supported map controls.
Support for MapXtreme 9.2.0
The MapXtreme map control has been updated from version 8.1.0 to 9.2.0. This provides a number of bug fixes, as well as some new projections, mostly in Australia. More details can be found at pitneybowes.com.
See Changing the Current Map Control for further information on supported map controls.

InfoWorks ICM has been updated to leverage MapXtreme 9.2.0 which provides a number of benefits, but due to incompatibility between MapXtreme 9.2.0 and MapXtreme 8.1.0 components (used in InfoWorks ICM
Attribute names and graph numbers now included in Trace titles
For Object per Page and the Simulation per Page types of custom graphs, the titles of graph traces now include the name of the attribute that is being graphed as well as the number of the graph in which the trace is displayed. The trace titles can still be changed using the Trace Style dialog.
Importing rainfall events
The import of rainfall events from generic CSV files has been enhanced and now supports a significantly wider range of CSV formats.
Design rainfall for SWMM simulations
Design rainfall is now available for events in SWMM simulations.
Sub-events for rainfall events in SWMM simulations
Previously, the engine that is used for processing SWMM simulations treated all the times in the event, regardless of any division into sub-events, as a constant stream of data. This no longer applies to rainfall events; sub-events for rainfall events in SWMM simulations are now treated in the same as they are for InfoWorks simulations. See the Events topic for further information.
Manning's N roughness coefficient for SWMM conduits
Two roughness coefficient - Manning's N or Low depth Manning's N can now be specified for a conduit in a SWMM network.
A new Low depth Manning's N field has been added to conduit properties for all conduits except those with an Irregular, Force Main or Dummy shape. The new Depth threshold field enables you to specify the depth that determines which conduit roughness coefficient- Manning's N or Low depth Manning's N - is to be applied to the entire conduit. When the flow is equal or greater than the depth threshold, the roughness Manning's N coefficient is used. When flow is less than the depth threshold, the Low depth Manning's N coefficient is used.
No values will be assigned to the Low depth Manning's N and Depth threshold fields for existing conduits, but for all new conduits, these fields will be assigned the defaults values of 0.010 and 0 respectively.
Infiltration modelling for Subcatchments (SWMM)
The way in which the infiltration of rainfall into the upper soil zone of a subcatchment in a SWMM network is to be modelled can now be set for each subcatchment as well as at the network level.
A new Infiltration model parameter has been added to the subcatchment properties which allows you to choose a particular infiltration model that is to be applied to the subcatchment or you can choose to use the model that is set for the network. See the Subcatchment Data Fields (SWMM) and the Soil Infiltration (SWMM) topics for further information.
Each subcatchment in a SWMM network can now also be associated with different soils, each of which has its own set of infiltration characteristics. Each soil can also be associated with any number of subcatchments. However, only the infiltration parameters for each soil, which are applicable to the selected infiltration model, will be applied during a simulation.
See the Soil Infiltration (SWMM), Soil Data Fields (SWMM), and Subcatchment Data Fields (SWMM) topics for further information.
Additional DWF inflows for SWMM nodes
You can now specify dry weather flow of additional inflows to nodes in a SWMM network. A new Additional DWF field has been added to the node properties, which allows you to specify a constant baseline value for any additional inflow you want to model as well as up to four time patterns that can be used to adjust the base flow value. When running simulations, ICM will add all the DWF flows, and all the DWF concentrations for a given pollutant, and then multiply the total flow by the total concentration to provide the DWF load for each node in the applicable network.
Initial state simulations for SWMM networks
A network state from a previous SWMM simulation can now be used as the initial state for the first simulation in a run. A new drop target, Sim providing initial state, has been added to the SWMM Run view. You can drag a simulation, whose state has been saved, from the Explorer window, and drop it into this target.
A new Save state at end of simulation check box has also been added to the view. This can be used to indicate whether or not the state of a simulation should be saved when the simulation is complete.
See the Schedule Hydraulic Run View (SWMM) topic for further information.
Impervious and pervious runoff results for SWMM Subcatchments
Impervious and pervious runoff depths are now included in the subcatchment simulation results.
Summary results for SWMM simulations
Summary results for SWMM simulations are now available in InfoWorks ICM.
Water quality results for SWMM simulations
The results of the build-up and washoff of pollutants in nodes, conduits and subcatchments for SWMM simulations are now included in the node results, link results and subcatchments results respectively.
See the Build-up/Washoff Models topic for details about how pollutant build-up and washoff are calculated.
Reporting of average results for nodes and links in a SWMM run
You can now choose to include average results for nodes and links in the output text report. A new check box, Average results, has been added to the Schedule Hydraulic Run View (SWMM). If the box is checked, time series results for nodes and links will be reported as average values computed over a reporting time step. If unchecked (default), the results will be interpolated point values at the end of the reporting time step.
Importing InfoSWMM model networks
Model data from InfoSWMM networks can now be imported to SWMM networks in InfoWorks ICM. See Importing InfoSWMM Data to SWMM Networks for further information.
Exporting SWMM network data
A SWMM network can now be exported to CSV files, Snapshot files and GIS file formats (Geodatabase, MIF, SHP and TAB) or by using the Open Data Export Centre. You can either export a SWMM network using one of the various Export options in the Network menu or by right-clicking on a SWMM network in the Explorer window and choosing the relevant Export option from the context menu.
Exporting results for SWMM simulations to GIS file formats
Two additional menu options, Export to GIS and Export maxima to GIS, are now available in the Results menu for SWMM networks.
The Export to GIS option enables one or more time varying and maximum results from SWMM simulations to be exported to MIF, SHP, or TAB file format or to a Geodatabase. Whilst the Export maxima to GIS enables the export of maximum results from SWMM simulations to MIF, SHP, or TAB file format or to a Geodatabase.
See Exporting Results to GIS for further information.
Encoding systems for SWMM5 network data import and export
It is now possible to choose the ASCII, UTF-8 or UTF-8 BOM encoding system when importing and exporting SWMM5 network data to or from a SWMM network. UTF-8/UTF-8 BOM is of particular relevance to customers using non-Western Latin characters.
SWMM5 network data imports to SWMM networks
The following changes have been made when importing SWMM5 network data from SWMM5 text files to SWMM networks:
- AVERAGES from the [REPORT] section can now be imported to the Average results check box in a SWMM Run.
- Data from the [Innovyze_Supplementry_DryWeatherFlow] section, if present, is now imported to a SWMM Node network object in InfoWorks ICM. If Type is Flow, the data is imported to an ICM SWMM node's Additional DWF grid. If Type is not flow, the data is imported to the node's Pollutant DWF grid.
- Data from the [Innovyze_Supplementary_Infiltration] section, if present, is now imported to a SWMM Subcatchment network object in InfoWorks ICM.
SWMM network data exports to SWMM5 text files
The following changes or additions have been made when exporting SWMM network data to SWMM5 text files:
- The values in the Baseline column in an ICM SWMM node's Additional DWF grid are exported to the Base parameter in the [Innovyze_Supplementary DryWeatherFlow] section of a SWMM5 text file, and the Base flow pattern 1 - Base flow pattern 4 column values are exported to the Pat 1 to Pat 4 parameters in the SWMM5 file. The Type is automatically set as Flow.
- Data from the Pollutant DWF grid for an ICM SWMM node is now exported to either the [DWF] or the [Innovyze_Supplementary DryWeatherFlow] section of a SWMM5 text file. The first instance of any type of pollutant is exported to the [DWF] section while any other instances of the same type of pollutant (i.e. same pollutant name) are exported to the [Innovyze_Supplementary DryWeatherFlow] section of the file.
- The new Infiltration model field in a Subcatchment is exported to the [Innovyze_Supplementary_Infiltration] section of the SWMM5 text file if set to an option other than Default. If the Infiltration model is not set or set to Default, the type of infiltration model is exported as part of the ICM Model Parameters Options data to the [OPTIONS] section in the exported file.
- If the Infiltration model is set to Horton, Modified Horton, Green Ampt, Modified Green Ampt or Curve number, the relevant subcatchment's infiltration parameters assigned via the Soils grid are exported to the [Innovyze_Supplementary_Infiltration] section. The exported values for the applicable soil infiltration parameters will be adjusted based on the percentage area of the subcatchment assigned to the soil. If the soils apply to less than 100% of the subcatchment area, and if any applicable parameters are specified in the non-soil infiltration section of the subcatchment's properties, then these will also be exported and adjusted for the remaining area.
See the SWMM5 Network Export from a SWMM Network topic for further information.
Node and link name generation
Automatic node and link name generation is now available for SWMM networks using the Name generation option from the Network menu. Note that the addition of this has resulted in a couple of minor cosmetic changes for InfoWorks networks; the option has been renamed from Node naming options... to Name generation and the Node Name Generation tab on the Name generation dialog has been changed to Nodes.
The functionality has not been altered in any way. See the Name Generation Dialog topic for further information.
Object type variable for node and link name generation
A new variable, {T}, can be used to append the object type to the name of a node or
Improvement in pre-processing speeds for spatial time series databases
Under certain spatial rainfall conditions, especially for large cell counts, the pre-processing times have been improved noticeably.
New data source for scalar TSDB
A new data source type for observed data, ADS Telemetry, has been added to scalar TSDBs. This allows you to connect to the ADS flow monitoring website in order to access the location and entity data you may want to include in a TSDB.
To use the ADS flow monitoring data, ensure that you select the ADS Telemetry option in the Type field in the Data Sources tab for the TSDB, specify the URL for the website in the Server and Database fields, enter your user key in the Password field, and then complete the other fields as required.
The Table and Data column fields on the Observed tab will contain a list of locations and entities that have been downloaded from the ADS flow monitoring website which you can assign to the applicable datastreams.

What's New in Version 1.5 - February 2011
What's New in Version 2.0 - August 2011
What's New in Version 2.5 - February 2012
What's New in Version 5.0 - May 2014
What's New in Version 5.5 - November 2014
What's New in Version 6.0 - April 2015
What's New in Version 6.5 - November 2015
What's New in Version 7.0 - May 2016
What's New in Version 7.5 - November 2016
What's New in Version 8.0 - May 2017
What's New in Version 8.5 - November 2017
What's New in Version 9.0 - May 2018
What's New in Version 9.5 - November 2018